You are here
Lesson 1: Food Chain
The rainforest food chain starts with the sun. It’s a solar powered system!
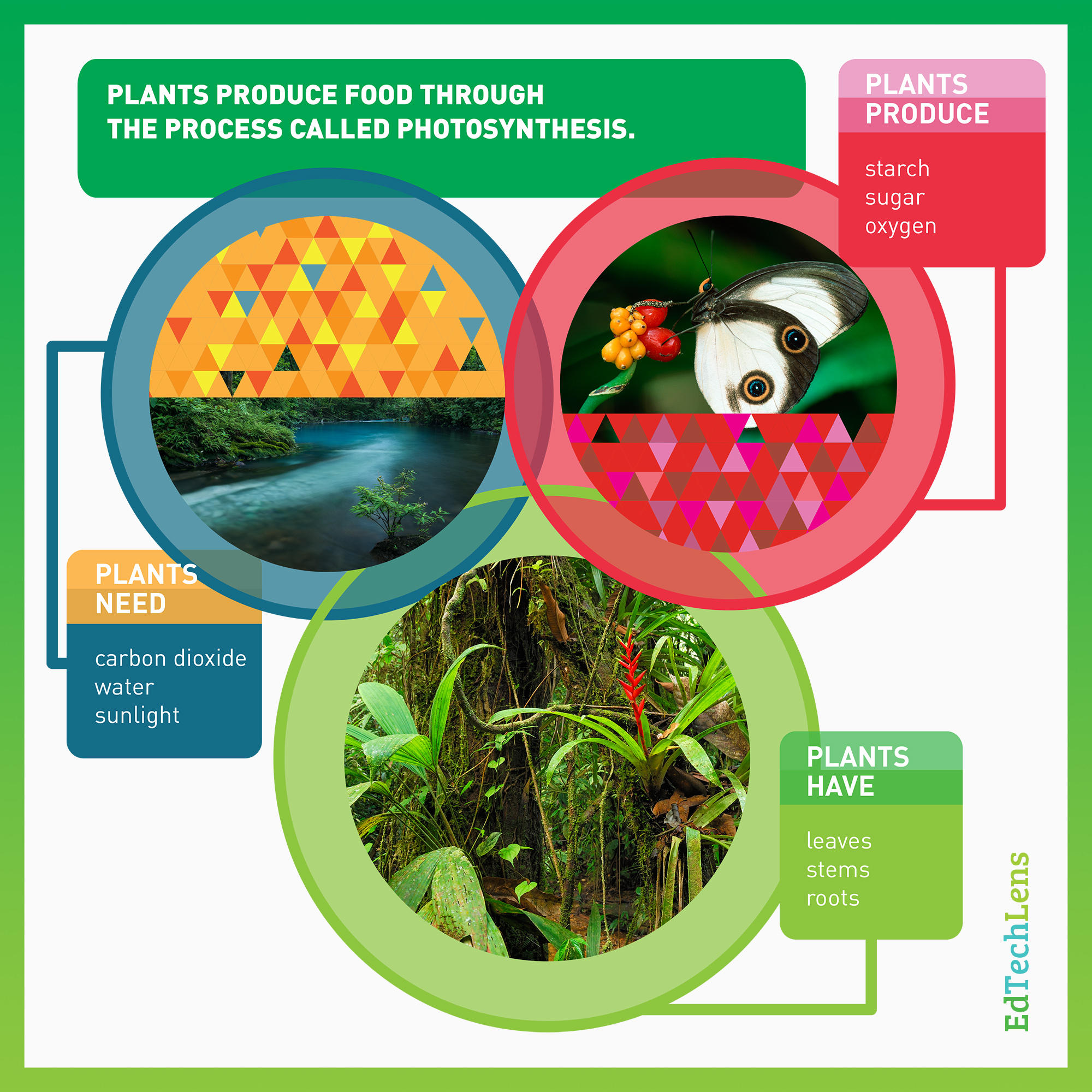
Plants are producers. This means they produce or make their food.
Here is their recipe — add light to water and carbon dioxide to make healthy food. But the plants need all three things to be able to make their food. Leaves have the job of collecting sunlight.
Leaves are a plant’s food-making factories. Green leaves are where photosynthesis happens. Tiny pores in the leaves let in air while water arrives after traveling up from the plant’s roots. When the sun shines on the leaf, photosynthesis starts. Sunlight powers the change of air and water into sugar. The sugar is the plant’s food; it’s the energy the plant needs to live and grow. It’s also the energy passed onto animals that eat the plant.
Animals are consumers. Their energy comes from what they eat.
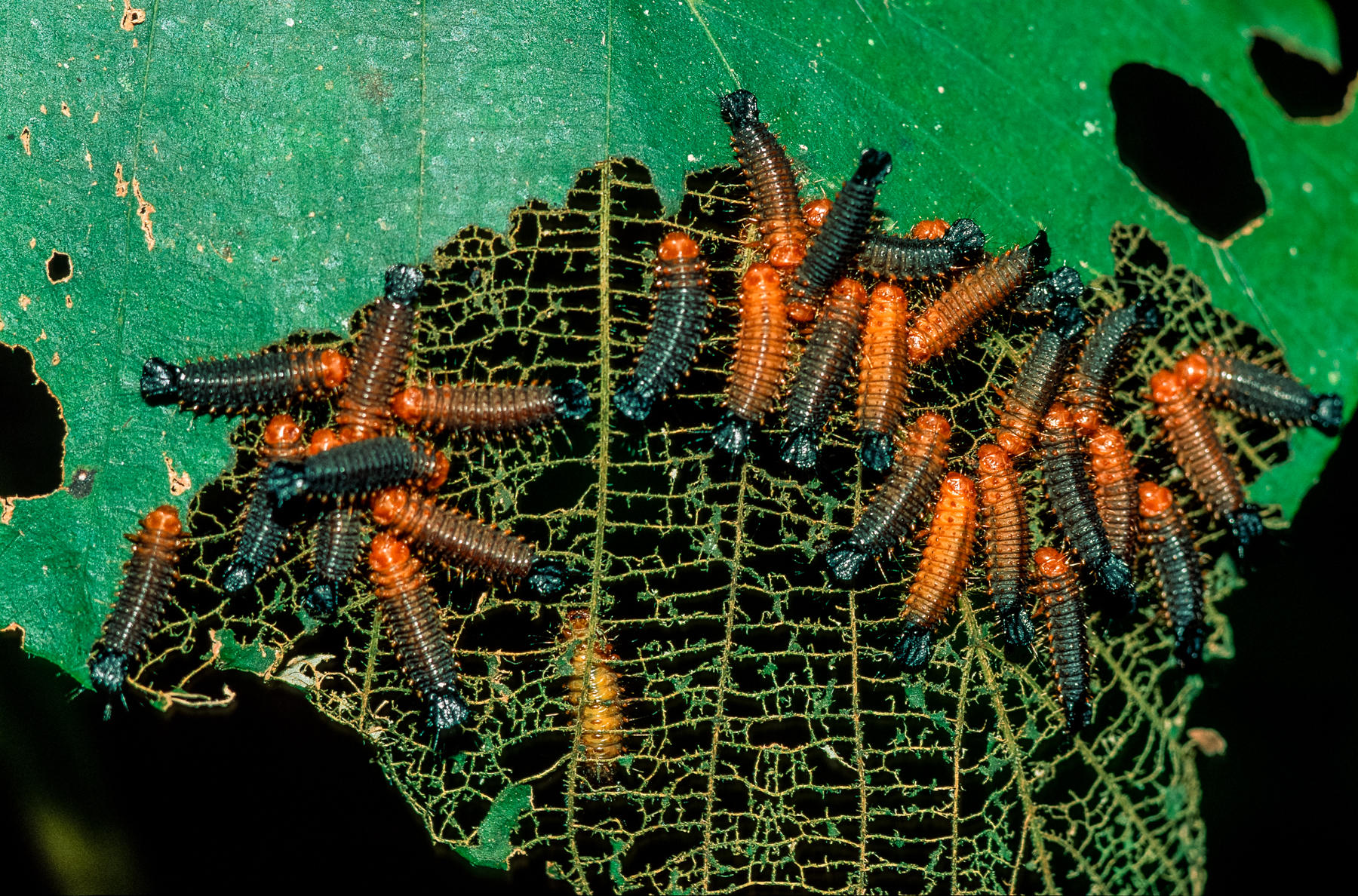
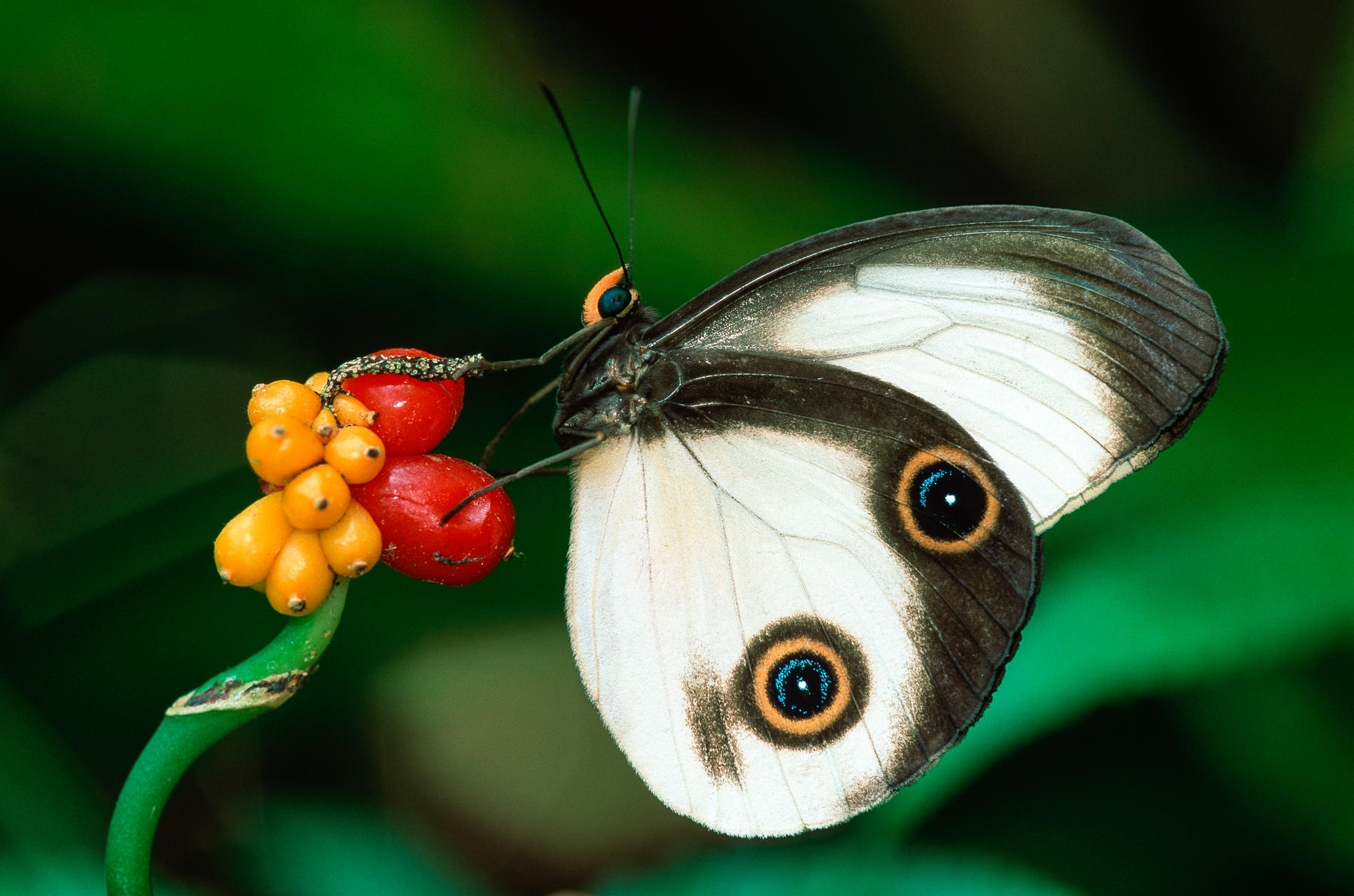


Producers and consumers both live in the rainforest.
Plants are producers because they make their own food. They grow by taking in sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide and then changing that energy into food. Animals are consumers because they cannot make their own food. So they must find it in other places. Here in this photo, these insect larvae power their bodies with the energy they get from eating leaves.
Babies must eat different food than grown-ups — this is because they can only take in certain kinds of nutrients. Some insects in the rainforest are similar in the ways they eat. As larvae, they may eat one part of a plant. As they grow older, they may begin eating other parts of different plants. Many caterpillars feed on leaves when they are young. Some even eat only one type of leaf. But after the caterpillars change into butterflies, they feed on the nectar from flowers.
Some animals eat plants and others eat other animals, but all are consumers.
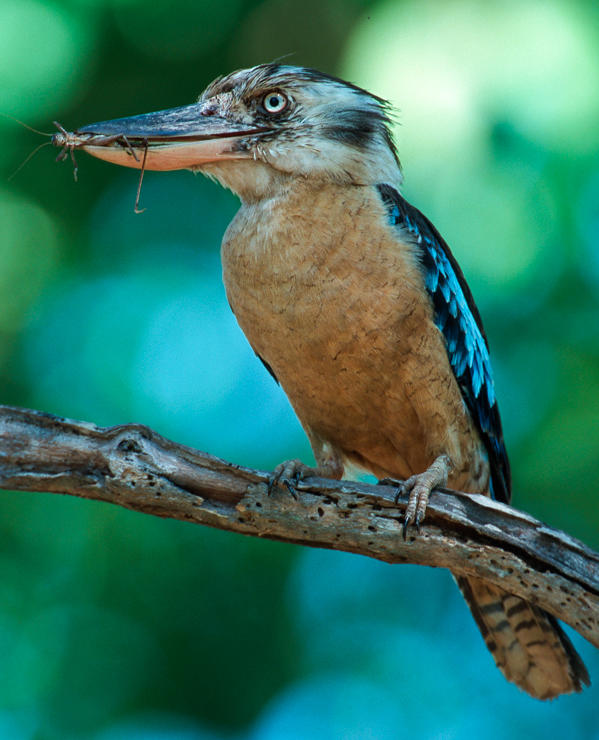


All animals are consumers. But that does not mean they all eat the same things.
Animals that do not eat meat and eat only plants are called herbivores. This group includes some insects, mice, many birds, and capybaras. Animals that eat meat are called carnivores. Alligators, jaguars, spiders, and some birds are examples of carnivores.
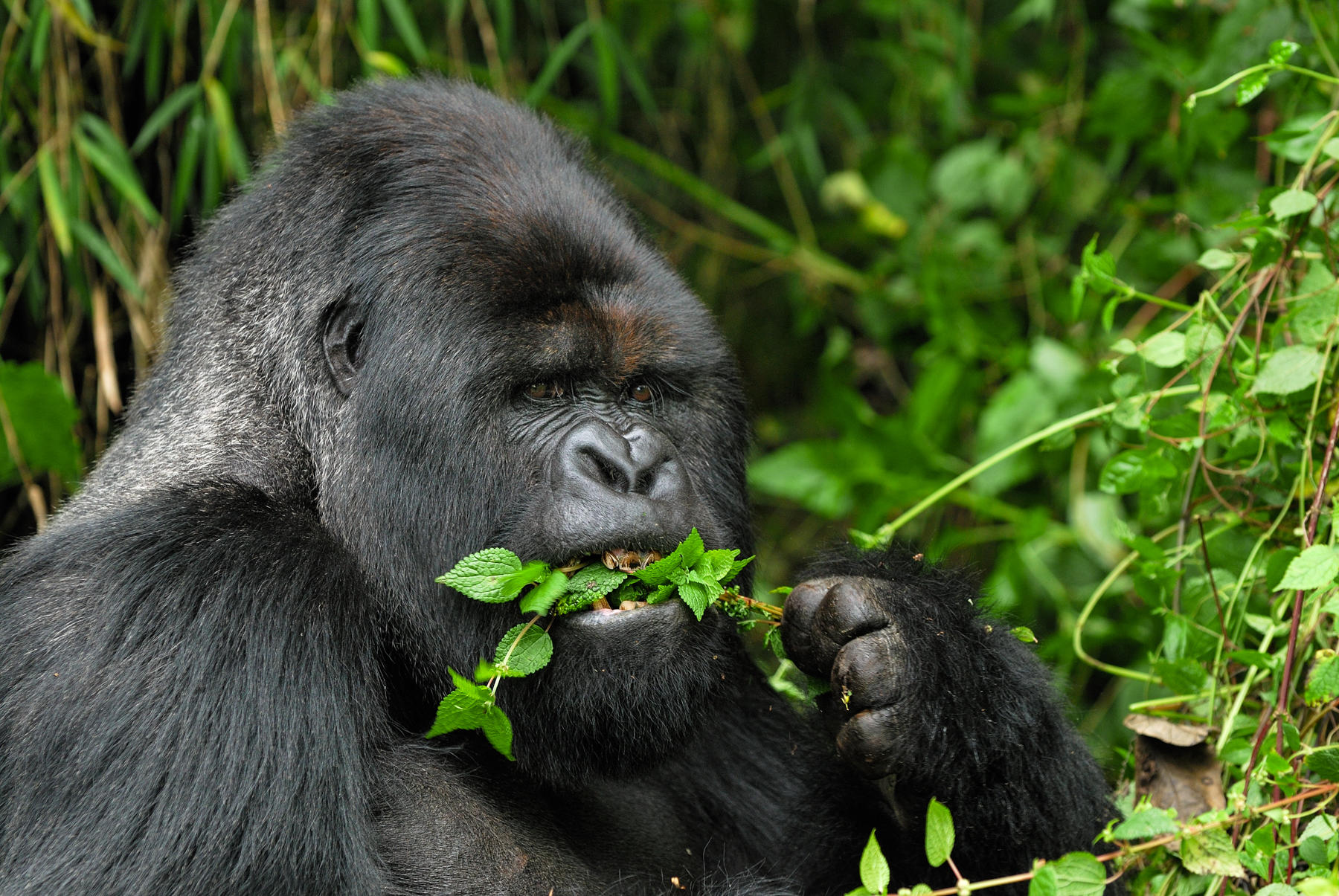
You now know about carnivores and herbivores. Carnivores eat only meat and herbivores eat only plants. But there are many animals that need to eat both plants and meat in order to survive. These animals are called omnivores. The mountain gorilla shown here is an herbivore. It likes to eat roots, tree bark, and fruit. Some birds are omnivores. You can find birds that eat fruit, insects, lizards, and small bird eggs. Their sharp bills help them pick fruit from trees and sometimes toss it to other bird friends.
Fungi are important decomposers that return nutrients to the soil.
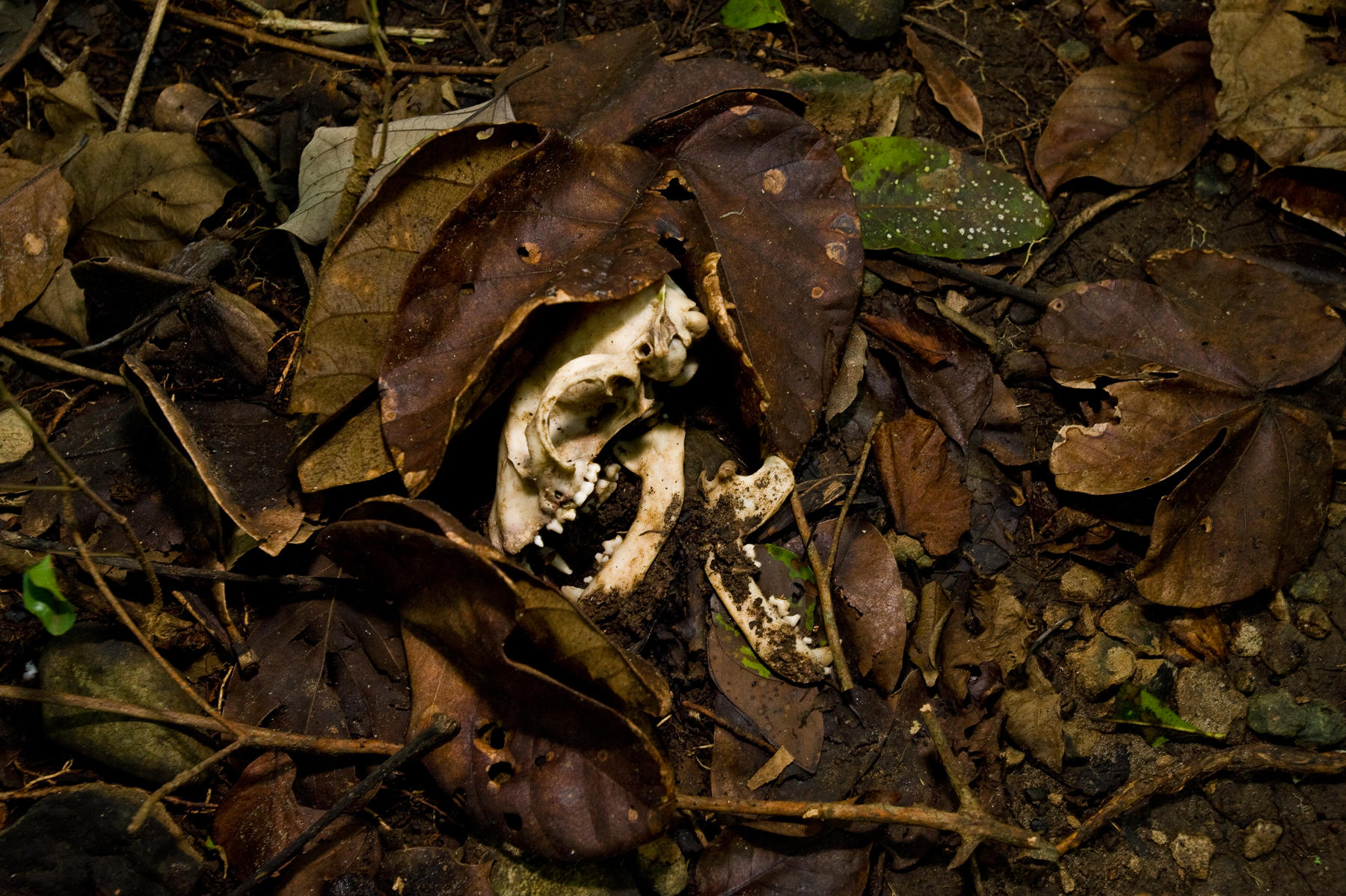


Nothing in nature lives forever. But what happens to the energy in an organism when it dies? The energy does not disappear; instead it is returned to the environment.
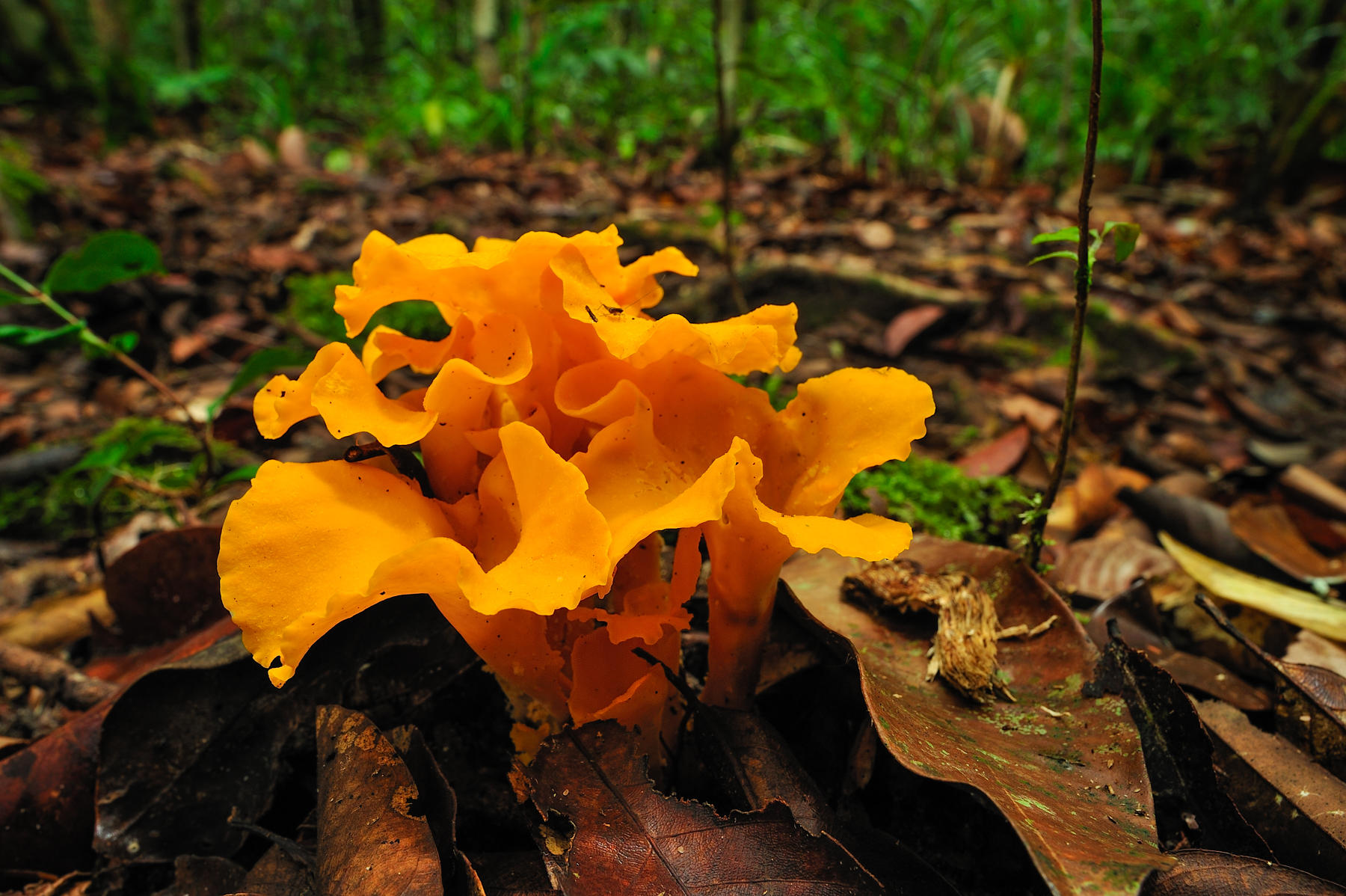
When plants and animals die, a process known as decomposition begins. Here's what happens: molds, fungi, and bacteria break down the plants and animals into smaller pieces. Some insects help out, too. These pieces then become part of the soil. The pieces help make the soil rich in nutrients. The nutrients then feed the trees and plants on the forest floor. This bright orange fungus helps with the decomposition process.
Organisms need help to do their job as decomposers. In order for decomposition to take place, heat, air, and water are necessary. The climate of a region also makes a difference, too. For instance, it is warm and moist on the forest floor. This means that dead plants and animals decompose very, very quickly. This is quite different from places that are cold or dry such as a tundra or a desert. In these places, decomposition takes much longer because it is not as wet.